- 1. Understanding XDR: How It Works and Why It's Important
- 2. The Evolution of Cybersecurity: From Endpoint Protection to XDR
- 3. What Are the Benefits of XDR?
- 4. Preparing and Implementing XDR: Best Practices and Key Considerations
- 5. XDR and the Future of Cybersecurity: What to Expect
- 6. XDR Security FAQs
What is Extended Detection and Response (XDR) Security?
Extended detection and response (XDR) is a security solution that uses multiple data sources such as endpoints, networks, identity, and cloud environments to detect and respond to cybersecurity threats. XDR solutions are designed to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's security posture and to improve threat detection and response capabilities.
Get the Full Audiobook to Boost Your XDR Knowledge
Understanding XDR: How It Works and Why It's Important
XDR is important because it provides a more holistic approach to threat detection and response. Traditional security solutions, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) or network detection and response (NDR), only provide visibility into specific areas. XDR, on the other hand, provides a unified view across multiple data sources, which enables more effective security outcomes.
XDR works by normalizing and analyzing security data from key sources across including but not limited to endpoints, networks, cloud environments, identity solutions, and applications. XDR applies advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to understand how security telemetry is related, for the purpose of preventing attacks and identifying, investigating, and remediating potential threats.
XDR solutions provide a centralized view of an organization's security posture and threat landscape, which enables security teams to quickly identify and investigate potential threats. The integration of data from multiple sources allows for a more comprehensive understanding of an attack, enabling faster and more effective incident response. Automated response actions, such as quarantining an endpoint or blocking an IP address, which can be triggered based on predefined rules or machine learning models are also capabilities. This automation can significantly reduce response times and allow security teams to focus on more complex tasks.
The Components of XDR
The components of XDR vary by vendor and solution but typically include the following:
- Data sources integrate and analyze data from multiple sources, such as endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and applications. The more data sources that can be integrated, the more comprehensive the XDR solution can be.
- Analytics and machine learning algorithms to correlate and analyze data from multiple sources. This enables the solution to identify potential threats and prioritize them based on risk.
- Threat intelligence, which provides up to date information on the latest threats and attack techniques. This enables the solution to better detect and respond to new and emerging threats.
- Incident response including automated response actions, such as quarantining an endpoint or blocking an IP address. These actions can be triggered based on predefined rules or machine learning models, enabling faster and more effective incident response.
- A centralized dashboard that displays security events and alerts from multiple sources. This enables security teams to quickly identify and investigate potential threats.
- Integration with other security solutions such as security information and event management (SIEM) systems and endpoint protection platforms.
The Evolution of Cybersecurity: From Endpoint Protection to XDR
The evolution of cybersecurity has been driven by the changing nature of cyberthreats and the need for more comprehensive security solutions. Traditionally, organizations have relied on endpoint protection solutions, such as antivirus software, to defend against cyberthreats. These solutions were designed to protect individual endpoints, such as desktops and laptops, from malware and other types of attacks.
However, as cyberthreats became more sophisticated and targeted, traditional endpoint protection solutions became less effective. Attackers began using advanced techniques such as fileless attacks, which bypass traditional endpoint protection solutions.
To address these challenges, organizations began adopting EDR solutions, which provided greater visibility into endpoint activity and enabled faster incident response. EDR solutions used advanced analytics and machine learning to detect and respond to threats, and provided more detailed information on threat activity.
Traditional Endpoint Protection
Traditional endpoint protection is a type of cybersecurity solution that focuses on protecting individual endpoints, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices, from malware and other types of cyberthreats. These solutions typically use signature-based detection to identify known threats and heuristic analysis to detect novel threats.
The primary goal is to prevent malware from infecting endpoints and compromising an organization's network. This is typically done through the use of antivirus software, which scans files and processes for known malware signatures.
In addition to antivirus software, traditional endpoint protection solutions may also include other features such as firewall protection, intrusion prevention, and device control. Firewall protection is used to block unauthorized access to an endpoint, while intrusion prevention is designed to detect and prevent network-based attacks.
Device control features can be used to restrict the types of devices that can be connected to an endpoint, such as USB drives or external hard drives, in order to prevent the spread of malware.
Limitations of Traditional Endpoint Protection
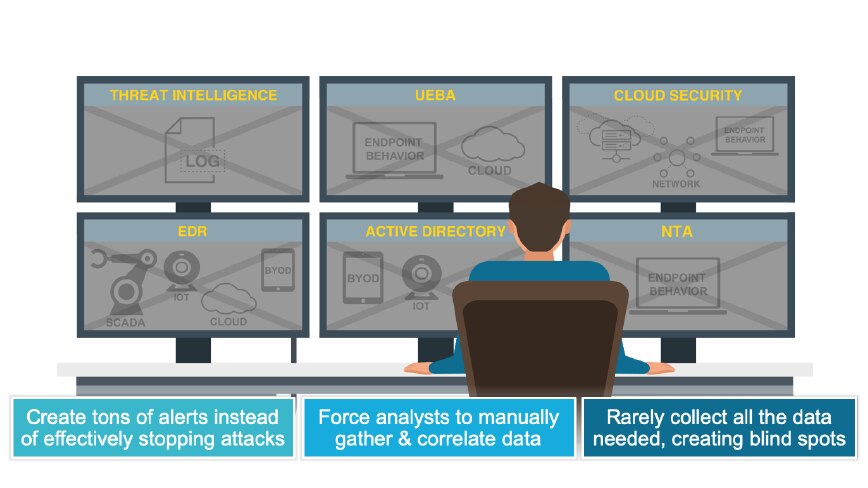
While traditional endpoint protection solutions are an important part of an organization's cybersecurity strategy, they do have some limitations. Some of the key limitations follow.
Limited Threat Detection
Traditional endpoint protection solutions rely primarily on signature-based detection to identify known threats. This means that they may be less effective at detecting new and emerging threats that do not have a known signature. Additionally, some types of advanced threats, such as fileless malware, may not use a file to infect an endpoint, making them difficult to detect with traditional endpoint protection solutions.
False Positives
Legacy endpoint tools may generate a high number of false positives, which are alerts that indicate a potential threat but turn out to be harmless. These false positives can consume a significant amount of time and resources for security teams, who must investigate each alert to determine whether it represents a real threat.
Limited Visibility
Endpoint security is focused primarily on protecting individual endpoints, which means that they may provide limited visibility into the broader identity, network and cloud environments. This can make it difficult to identify and respond to threats that may be present in other parts of an organization's threat vectors.
Incomplete Protection
Existing endpoint solutions may not provide complete protection against all types of cyberthreats, particularly those that target applications, cloud environments, or other areas beyond individual endpoints.
Limited Response Capabilities
Traditional endpoint protection solutions may not have robust response capabilities, which can make it more difficult to quickly respond to and remediate threats. This can lead to longer dwell times, during which attackers can continue to operate undetected.
The Emergence of XDR
The emergence of XDR is a response to the evolving nature of cyberthreats and the limitations of traditional endpoint protection solutions. As cyberattacks have become more sophisticated and targeted, organizations have increasingly recognized the need for a more comprehensive approach to cybersecurity that can better detect and respond to potential threats.
XDR emerged as a way to address these challenges by integrating and analyzing data from multiple sources across an organization's infrastructure, such as endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and applications. By aggregating and correlating data from multiple sources, XDR solutions can provide a more holistic view of an organization's threat landscape, which can enable more effective threat detection and response and extended protection.
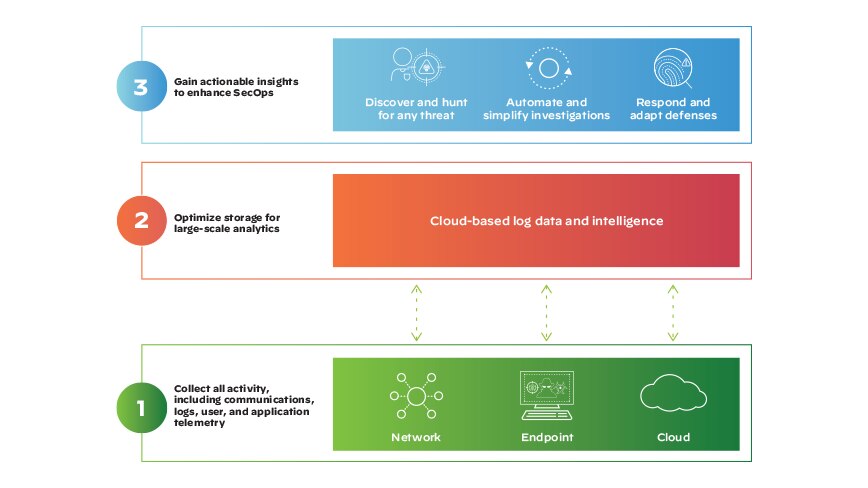
What Are the Benefits of XDR?
XDR solutions offer several benefits for organizations looking to improve their cybersecurity posture. Here are some of the key benefits of XDR:
- Comprehensive threat detection: Integrating and analyzing data from multiple sources can provide a more comprehensive view of the threat landscape. This can enable more effective threat detection and response, as potential threats can be identified and investigated more quickly and accurately.
- Faster incident response: Features such as automated response capabilities, can help to accelerate incident response times and reduce the amount of manual effort required to investigate and remediate potential threats. This can enable security teams to respond more quickly and effectively in the event of a security incident.
- Reduced false positives: XDR can help to reduce the number of false positives generated by traditional endpoint protection solutions, which can consume a significant amount of time and resources for security teams. By providing more accurate and relevant alerts, XDR solutions can enable security teams to more efficiently prioritize and respond to potential threats.
- Improved collaboration: XDR can facilitate greater collaboration between security teams, who may be able to work more closely together to investigate and respond to potential threats across the main threat vectors.
- Greater visibility: By identifying vulnerabilities and potential threats, XDR can help organizations to prioritize their security investments and allocate resources more effectively.
- Easier integration: Advanced XDR solutions offer increased time to value thanks to a large number of out-of-the-box integrations and fine-tuned detection algorithms across products.
More Comprehensive and Improved Threat Detection
XDR solutions can provide more comprehensive threat detection by integrating and analyzing data from multiple sources.
Broader Visibility
XDR can provide broader visibility into an organization's infrastructure, including endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and more. By collecting and analyzing data from multiple sources, XDR solutions can identify potential threats that might be missed by traditional endpoint protection solutions.
Correlation of Data
XDR can correlate data from different security tools and sensors, such as endpoint protection, network traffic analysis, and cloud security, to provide a more comprehensive view of an organization's security posture. By analyzing data from multiple sources, XDR solutions can identify potential threats more accurately.
Threat Hunting
XDR can enable threat hunting, which involves proactively searching for potential threats. By identifying potential threats before they become active, XDR solutions can help to prevent security incidents before they occur.
Threat Intelligence
XDR can incorporate threat intelligence feeds, which provide information on the latest threats and attack techniques. By incorporating this intelligence into their analysis, XDR solutions can identify potential threats more accurately and quickly.
Real-Time Monitoring
XDR can provide real-time monitoring, allowing potential threats to be identified and investigated as soon as they are detected. This can enable security teams to respond more quickly and effectively to potential threats, reducing the impact of a security incident.
Analytics and Machine Learning
XDR can use advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze data and identify potential threats. This can help to improve threat intelligence by providing more accurate and reliable detection of potential threats.
Automated Response
XDR may include automated response capabilities, which can help to accelerate incident response times and reduce the amount of manual effort required to investigate and remediate potential threats. By automating some of the response process, XDR solutions can enable security teams to respond more quickly and effectively to potential threats.
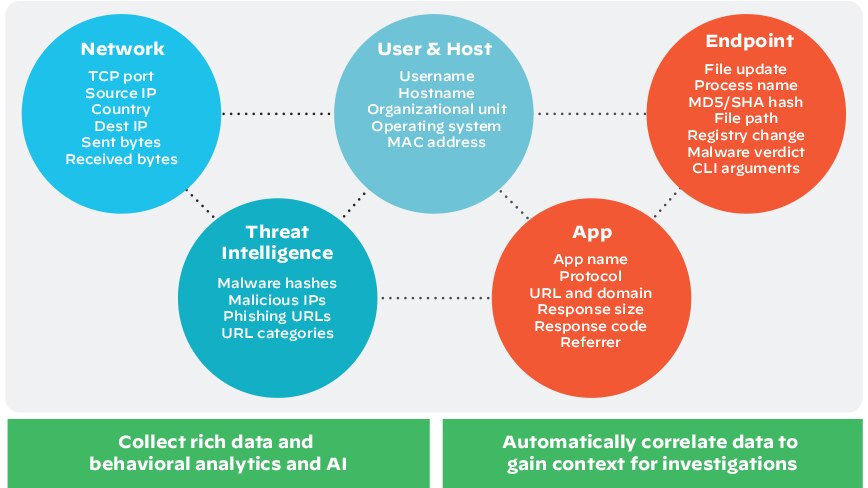
Streamlined Incident Response
XDR solutions can streamline incident response by providing more complete visibility and automating some of the incident response process. Here are some ways that XDR can enable more streamlined incident response:
- Centralized incident management: XDR can provide a centralized incident management console that allows security teams to manage incidents from a single location. This can help to reduce the time and effort required to manage multiple incidents.
- Automated response: Some incident response processes can be automated via XDR, such as quarantining a device or blocking an IP address. This can help to accelerate incident response times and reduce the amount of manual effort required to investigate and remediate potential threats.
- Prioritized alerts: Prioritizing alerts based on their severity and potential impact, XDR can help security teams to focus their attention on the most critical alerts first, enabling them to respond more quickly and effectively to potential threats. Further, by rolling alerts up into incidents, deeper context is delivered to security analysts, increasing productivity and efficiency.
- Incident timeline: XDR can provide an incident timeline that shows the sequence of events leading up to the incident. This can help security teams to understand the scope and impact of the incident more quickly, enabling them to respond more effectively.
Preparing and Implementing XDR: Best Practices and Key Considerations
Here are some best practices and key considerations to keep in mind when implementing an XDR solution:
- Define your security requirements: Before implementing an XDR solution, it's important to define your security requirements and objectives. This will help you to select the right XDR solution for your organization.
- Assess your current security infrastructure: Evaluate your current security infrastructure to identify potential gaps and areas for improvement. This will help you to identify which areas will need to be integrated into the XDR solution.
- Evaluate XDR vendors: When evaluating XDR vendors, look for those that have a proven track record of delivering effective detection and response capabilities. It's also important to ensure that the XDR solution integrates with your existing security environment.
- Plan for data integration: XDR solutions require data from multiple sources, such as endpoint protection, network traffic analysis, and cloud security. It's important to plan for how this data will be integrated into the XDR solution to ensure that the solution is effective.
- Establish incident response procedures: XDR solutions can provide faster and more comprehensive threat detection, but it's important to have a well-defined incident response plan in place to ensure that incidents are responded to quickly and effectively.
- Consider the cost: XDR solutions can be costly, so it's important to consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating XDR solutions. This includes not only the initial purchase cost but also ongoing maintenance and support costs.
- Train your staff: XDR solutions require trained security staff to effectively manage and respond to incidents. Ensure that your staff is trained on how to use the XDR solution and how to respond to potential threats.
- Plan for ongoing monitoring and optimization: XDR solutions require ongoing monitoring to ensure that they are effective in detecting and responding to potential threats. It's important to plan for ongoing monitoring and optimization to ensure that the XDR solution remains effective over time.
Implementing XDR Agents and Connectors
Implementing XDR agents and connectors is an important part of deploying an XDR solution. The following is an overview of what's involved.
XDR Agents
An XDR agent is a lightweight software component that is installed on endpoints, servers, or other devices in the environment. The agent is responsible for collecting security data, such as endpoint telemetry, network traffic, and application logs, and transmitting that data to the XDR platform for analysis.
To implement XDR agents, you will need to:
- Identify which endpoints, servers, or other devices will require an XDR agent.
- Install the XDR agent software on those devices.
- Configure the XDR agent to collect the security data and transmit it to the XDR platform.
- Test the XDR agents to ensure they’re properly collecting and transmitting security data.
XDR Connectors
An XDR connector is a software component that integrates with existing security tools and data sources, such as SIEM systems, endpoint protection platforms, and cloud security tools. The connector is responsible for collecting security data from these sources and transmitting it to the XDR platform for analysis.
To implement XDR connectors, you will need to:
- Identify which security tools and data sources will require an XDR connector.
- Install the XDR connector software on those systems.
- Configure the XDR connector to collect the security data and transmit it to the XDR platform.
- Test the XDR connectors to ensure they’re properly collecting and transmitting security data.
Configuring and Tuning XDR Analytics
Configuring and tuning XDR analytics is an important aspect of implementing an XDR solution. Here's an overview of what's involved:
- Define use cases: Before configuring XDR analytics, it's important to define the use cases that the solution will address. For example, you may want to detect malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, or data exfiltration. Defining use cases will help you to focus your XDR analytics configuration on the most critical threats.
- Define detection rules: Once you have defined your use cases, you will need to define the detection rules that will be used to identify potential threats. Detection rules typically consist of a set of conditions that must be met in order for a potential threat to be identified. For example, a detection rule may trigger an alert if a user attempts to access a sensitive resource outside of business hours.
- Configure response actions: XDR analytics can trigger a range of response actions, such as blocking a user or device, quarantining a file, or alerting a security team. It's important to configure response actions carefully to ensure that they are appropriate for the specific threat.
- Configure alerts: XDR analytics can generate alerts when potential threats are identified. It's important to carefully configure alerts to ensure that they are not too noisy, but also not too quiet. You may need to fine-tune alerts over time based on your organization's specific needs.
- Monitor performance: Once XDR analytics have been configured, it's important to monitor their performance over time. This may involve analyzing false positives and false negatives, as well as identifying areas where XDR analytics can be improved.
Integrating XDR with Your Existing Security Infrastructure
Integrating XDR with an existing security infrastructure is an important aspect of deploying an XDR solution. Here are some steps you can follow.
Evaluate Your Current Security Infrastructure
Start by evaluating your current security infrastructure to identify potential integration points for XDR. This may include SIEM systems, endpoint protection platforms, cloud security tools, and other security solutions.
Identify Integration Options
Once you have identified potential integration points, you will need to identify the integration options available for each system. This may include application programming interfaces (APIs), software development kits (SDKs), or other integration options.
Configure Integrations
After identifying the available integration options, you will need to configure the integrations between XDR and your existing security infrastructure. This may involve configuring APIs, installing connectors, or other configuration tasks.
Test Integrations
Once the integrations have been configured, it's important to test them to ensure that data is being exchanged correctly between XDR and your existing security infrastructure. This may involve conducting penetration testing, analyzing log data, or other testing methods.
Monitor Integrations
After the integrations have been configured and tested, it's important to monitor them over time to ensure that they continue to function correctly. This may involve monitoring log data, analyzing system performance, or other monitoring tasks.
XDR and the Future of Cybersecurity: What to Expect
There are four potential developments we can expect from XDR and the future of cybersecurity:
- Increased adoption of XDR: As organizations continue to face increasingly complex and sophisticated cyberthreats, the adoption of XDR solutions is likely to increase. XDR solutions offer a more comprehensive and integrated approach to detection and response, which can help organizations better protect themselves against cyberattacks.
- Improved threat intelligence: XDR solutions are designed to provide organizations with more accurate and actionable threat intelligence. As XDR solutions continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities that help organizations stay one step ahead of cyberthreats.
- More automation: XDR solutions are designed to automate many aspects of threat detection and response, which can help organizations to respond more quickly and effectively to cyberattacks. As XDR solutions continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more automation capabilities that help organizations to reduce the workload on their security teams.
- Integration with other security technologies: XDR solutions are designed to integrate with other security technologies, such as endpoint protection platforms, cloud security tools, and SIEM systems.
Emerging Trends in XDR
As XDR solutions continue to evolve and mature, several emerging trends are shaping the future of this technology. Here are some of the key trends in XDR.
Cloud-Native XDR
As organizations continue to move their applications and data to the cloud, cloud-native XDR solutions are emerging to provide comprehensive detection and response capabilities across cloud environments. These solutions are designed to work seamlessly with cloud infrastructure and applications, providing organizations with a more comprehensive view of their security posture.
Deeper Integrations
XDR solutions are designed to integrate with other security technologies, such as endpoint protection platforms and SIEM systems. However, as XDR solutions continue to evolve, we can expect to see even deeper integrations that provide organizations with a more holistic view of their environment. For example, XDR solutions may integrate with identity and access management (IAM) systems to provide more granular visibility and control over user access.
Machine Learning and Automation
XDR solutions already use machine learning and automation to detect and respond to threats in real time. However, as these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more advanced capabilities, such as predictive analytics and automated response workflows.
Managed XDR
Some smaller organizations, or organizations with lean security teams may opt for a managed option. The right MDR provider brings expertise, focused telemetry and processes that deliver context, insights, and visibility so your team can make accurate, fast decisions to contain and mitigate threats.
Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust security is a security model that assumes all users, devices, and applications are untrusted and must be verified before being granted access to sensitive resources. XDR solutions can play a key role in implementing Zero Trust security by providing continuous monitoring and threat detection across all users, devices, and applications.
Open Standards
As XDR solutions continue to mature, we can expect to see increased adoption of open standards, such as STIX/TAXII, which allow for the sharing of threat intelligence across different security technologies and platforms. This can help organizations to improve their overall security posture by providing a more comprehensive and integrated view of threat intelligence.
The Evolution of XDR Capabilities
While AI and machine learning are important components of XDR, there are other capabilities that are also evolving to enhance the effectiveness of this technology. Here are some examples:
- Expanded data sources: XDR solutions are increasingly incorporating data from a wider range of sources beyond just endpoints, such as network traffic, cloud logs, and cloud APIs. This broader visibility enables XDR solutions to detect threats that might have gone undetected otherwise.
- Improved web interfaces: XDR solutions are also evolving to provide more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for security analysts. This includes features like customizable dashboards, automated workflows, and visualizations that help analysts quickly identify and respond to threats.
- Enhanced integrations: XDR solutions are designed to integrate with other security technologies, such as SIEM systems and endpoint protection platforms. These integrations are becoming more seamless and comprehensive, allowing for easier sharing of data and a more unified approach to security operations.
- Better automation: While machine learning and AI play a critical role in XDR, automation is also improving in other areas. For example, XDR solutions are increasingly automating incident response workflows, allowing security teams to respond to threats more quickly and effectively.
- Greater scalability: As XDR solutions continue to evolve, they are becoming more scalable and able to handle large volumes of data from diverse sources. This enables organizations to deploy XDR solutions across their entire infrastructure, including cloud environments and remote endpoints, to provide comprehensive protection against threats.
XDR and the Rise of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two critical components of XDR, as they enable this technology to detect and respond to threats in real time. There are several ways in which AI and ML are driving the evolution of XDR, including threat detection, automated response, contextual insights, adaptive threat hunting, and improved accuracy.
In terms of threat detection, XDR solutions use AI and ML to analyze massive amounts of data from a wide range of sources such as endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. This helps identify potential threats that traditional signature-based antivirus solutions may miss. Advanced analytics play a significant role in enhancing the detection capabilities of XDR solutions.
Once a threat is detected, XDR solutions apply AI and ML for an automated response. For instance, ML algorithms can be employed to analyze the behavior of a potential threat. This allows the XDR solution to automatically quarantine an infected endpoint or isolate a network segment, preventing the threat from spreading further.
AI and ML also contribute to providing contextual insights into security events. XDR solutions use ML algorithms to correlate threat intelligence from various sources, including public threat feeds, industry-specific intelligence, and internal security data. This offers deeper insights into the nature of a threat and informs the appropriate course of action.
Adaptive threat hunting is another aspect of XDR solutions that benefit from AI and ML. By using ML algorithms to learn from past incidents and identify patterns of behavior indicative of potential threats, XDR solutions can proactively identify and mitigate threats before they cause damage.
Lastly, AI and ML can help improve the accuracy of threat detection by reducing false positives and false negatives. By using advanced analytics to correlate data from multiple sources, XDR solutions can provide a more accurate picture of security events. This, in turn, reduces the amount of time security analysts spend investigating false alarms.
Additional Resources
XDR for Dummies guide
Listen to the XDR for Dummies Guide Audiobook
