- DSPM Market Size: 2025 Guide
- How DSPM Is Evolving: Key Trends to Watch
- How DSPM Combats Toxic Combinations: Enabling Proactive Data-Centric Defense
- What Is a Data Flow Diagram?
- What Is Data Exfiltration?
- What Is Data Movement?
- What Is a Data Breach?
- DSPM Tools: How to Evaluate and Select the Best Option
- How DSPM Enables XDR and SOAR for Automated, Data-Centric Security
-
What Is Data Detection and Response (DDR)?
- Data Detection and Response Explained
- Why Is DDR Important?
- Improving DSPM Solutions with Dynamic Monitoring
- A Closer Look at Data Detection and Response (DDR)
- How DDR Solutions Work
- How Does DDR Fit into the Cloud Data Security Landscape?
- Does the CISO Agenda Need an Additional Cybersecurity Tool?
- Supporting Innovation Without Sacrificing Security
- DSPM and Data Detection and Response FAQs
- What Is Data-Centric Security?
- What Is Unstructured Data?
- What Is Data Access Governance?
- DSPM for AI: Navigating Data and AI Compliance Regulations
- What Is Data Discovery?
- What Is Structured Data?
- What Is Shadow Data?
- How DSPM Enables Continuous Compliance and Data Governance
- What Is Data Classification?
- DSPM Vs. CSPM: Key Differences and How to Choose
- What Is Cloud Data Protection?
What Is DSPM?
Data security posture management (DSPM) is a comprehensive approach to safeguarding an organization's sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. DSPM encompasses various security measures, including data classification, data encryption, access control, data loss prevention (DLP), and monitoring. By implementing these measures, organizations can establish and maintain a robust data security posture, as required to meet privacy and security regulations, prevent data breaches, and safeguard their brand reputation.
Key Points
-
What is DSPM?
DSPM secures sensitive data (PII, PHI, PCI) across hybrid and multicloud environments by discovering, classifying, monitoring, and protecting data through policy enforcement and automated response. -
What visibility does DSPM provide?
It reveals where sensitive data lives, who accesses it, how it’s used, and the security posture of surrounding systems — including misconfigurations and drift. -
What are the stages of the DSPM lifecycle?
Discovery, classification, data flow mapping, access monitoring, risk assessment, policy enforcement, and incident remediation. -
Why is DSPM important?
It prevents breaches, detects shadow data, reduces insider risk, and supports compliance with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. -
What capabilities does DSPM offer?
Sensitive data discovery, contextual classification, access monitoring, policy enforcement, risk scoring, and automated remediation. -
How does DSPM differ from CSPM?
CSPM secures cloud infrastructure; DSPM secures the sensitive data within it. Both are essential for a complete cloud security strategy. -
What are common use cases for DSPM?
Shadow data detection, access audits, compliance enforcement, cloud data protection, and real-time threat response.
DSPM Explained
Data security posture management (DSPM) comprises the security practices and technologies that address security challenges stemming from the proliferation of sensitive data spread across diverse environments. An essential component of data security, DSPM provides organizations with an approach to protecting cloud data by ensuring sensitive and regulated data have the correct security posture, regardless of where the data resides or is moved to.
As a prescriptive, data-first approach to securing an organization's data assets in the cloud and on-premises, DSPM prioritizes the security of data — rather than just the systems where data resides. As such, DSPM is a critical component of a data security strategy, especially in cloud-first and cloud-native environments where traditional security controls fall short.
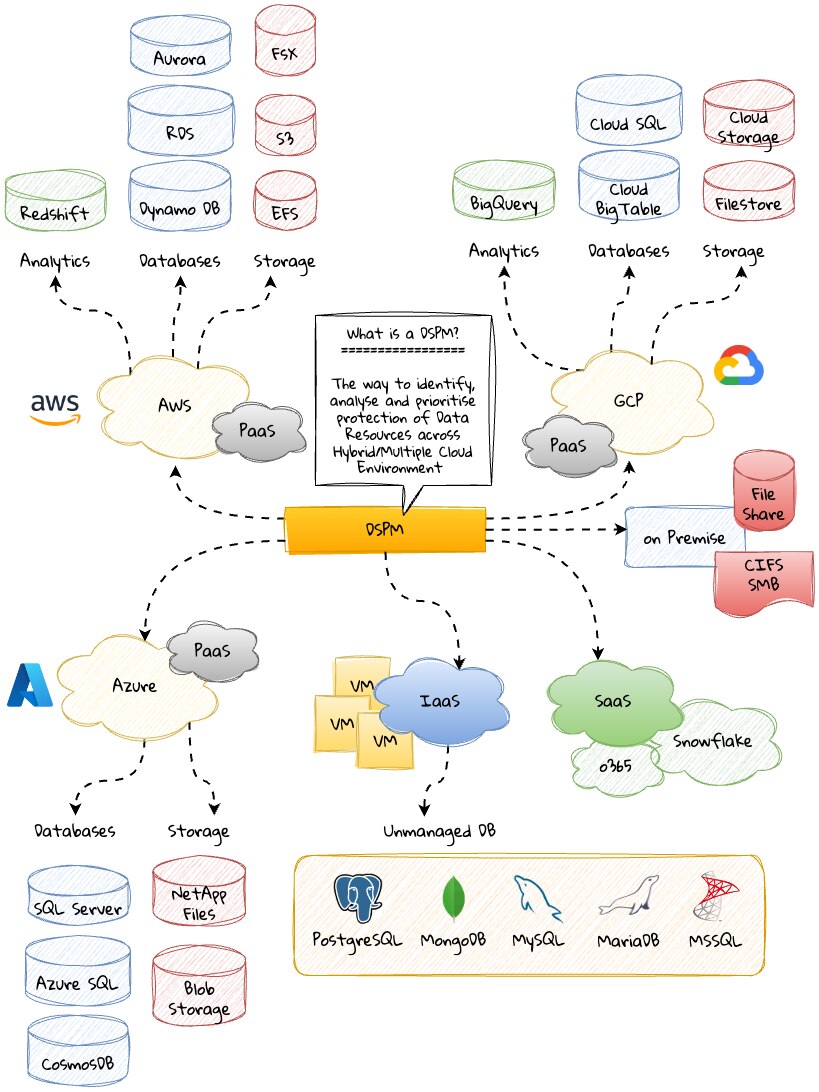
An emerging trend in cloud computing — covered by Gartner in its 2022 Hype Cycle for Data Security — DSPM technology automates data detection and protection to address the foremost challenge in secure data management — visibility. With it, organizations gain critical intel with the ability to see:
- Where sensitive data resides
- Who has access to it
- How data has been used
- What the security posture of the datastore or application is DSPM
How DSPM Works
DSPM uses data flow analysis to understand how data moves within an organization and to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities. Key steps involved in the DSPM process include:
Data Discovery
DSPM starts by locating and cataloging data sources throughout the organization — databases, file systems, cloud storage, third-party applications, etc. — to help organizations understand where their sensitive data resides.
Data Classification
Once the data sources are identified, DSPM classifies the data according to sensitivity and importance. Is the information personal identifiable information (PII), for example, financial data, or intellectual property? Data classification directs the prioritization of data protection efforts and aligns them with regulatory compliance requirements.
Data Flow Mapping
DSPM maps the flow of sensitive data between various components of the organization's infrastructure, such as servers, databases, and applications. A data flow diagram helps organizations to visualize how data is accessed, processed, and transmitted, providing insights into potential weak points and vulnerabilities.
Risk Assessment
By analyzing the data flow, DSPM identifies potential risks and vulnerabilities, such as unauthorized access, data leakage, or lack of encryption. Organizations can then prioritize their security efforts and address the most critical threats based on findings.
Security Control Implementation
Also based on the risk assessment, organizations can implement appropriate security controls to protect their data. Controls might include encryption, access control, and data loss prevention (DLP) techniques to ensure the security of sensitive data as it moves through the organization.
Monitoring and Auditing
Data security posture management continuously monitors the data movement to detect anomalies, potential threats, and policy violations. Regular audits help ensure that security controls are effective and the organization remains compliant with data protection regulations.
Incident Response and Remediation
In the event of a security incident, data posture management accelerates incident response by providing the necessary information to quickly identify affected data, assess the scope of the breach, and implement remediation measures to minimize the impact.
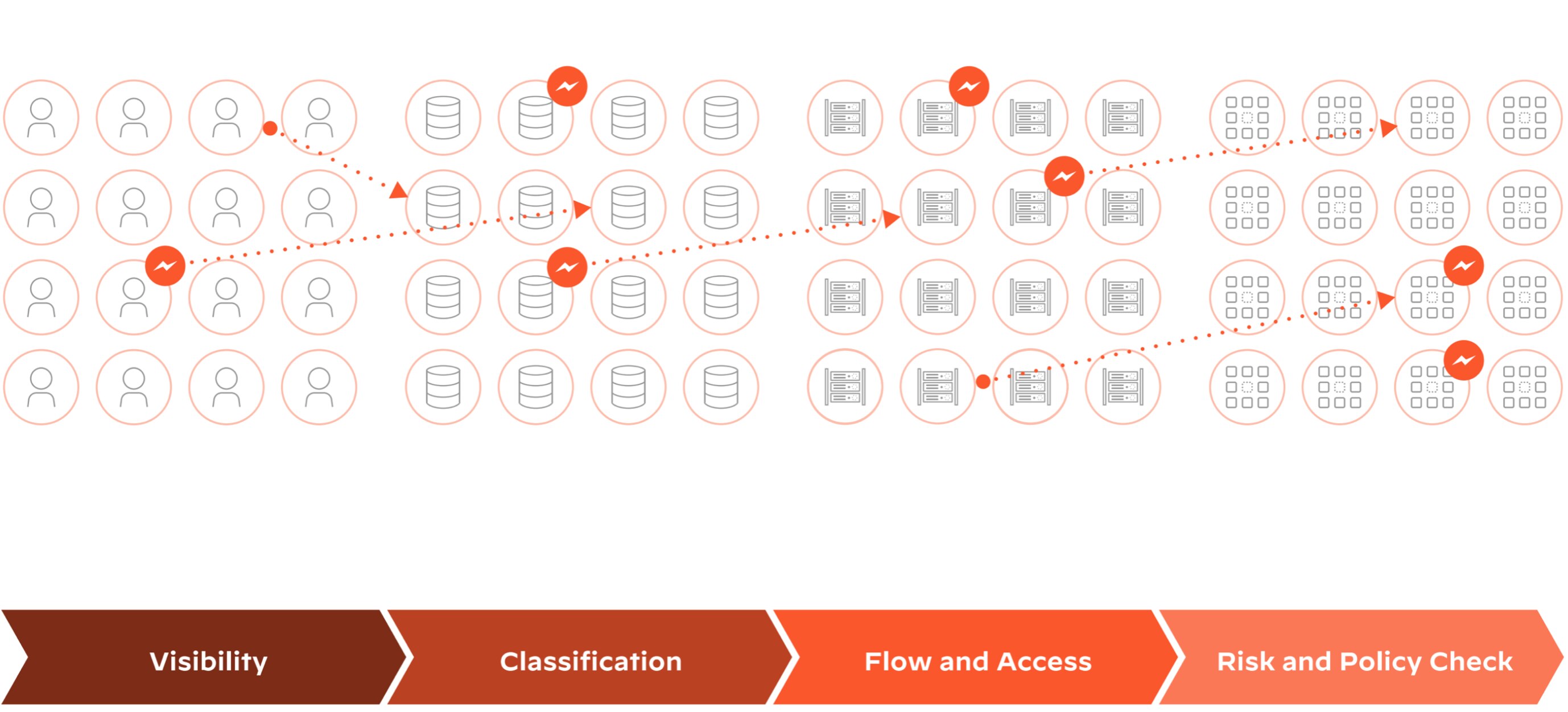
Figure 2: Data discovery, classification, and access governance
By utilizing data flow analysis, DSPM enables organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of how their sensitive data moves and interacts within their infrastructure. This understanding allows businesses to identify and address potential risks, ensuring the protection of their valuable data assets and maintaining regulatory compliance.
The Importance of Data Security Posture Management
The global datasphere is projected to grow by more than 50% — from 120 zettabytes (ZB) in 2023 to 181 ZB by 2025. It’s no wonder the idea of data breaches is keeping CISOs up at night. The combination of digital transformation processes, an increased appetite for data and analytics, and the proliferation of cloud datastores means enterprises are storing more sensitive data than they can effectively monitor or control.
Financial motives drive 94.6% of breaches. Data has always been a target for hackers, but the cost of recovering from breaches, specifically ransomware incidents that result in costs, has doubled in just two years, according to the 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR).
Related Article: Ransomware in the Cloud: Breaking Down The Attack Vectors
The importance of DSPM can’t be overstated, as it actively addresses the critical challenges and potential risks that organizations face in today's data-driven world.
Failure to implement DSPM can leave organizations exposed to security threats, putting valuable data assets at risk. Data breaches — which may involve loss of sensitive information, intellectual property, and trade secrets — damage brand reputation, often imposing long-term repercussions. Without prioritizing data posture, organizations can struggle to allocate resources effectively, particularly as it pertains to remaining responsive in a dynamic threat landscape. Collaboration between IT, security, and business teams breaks down, resulting in misaligned objectives and suboptimal security practices.
Conversely, by recognizing the importance of DSPM and incorporating it into their processes, organizations can create cohesive strategies to address their challenges.
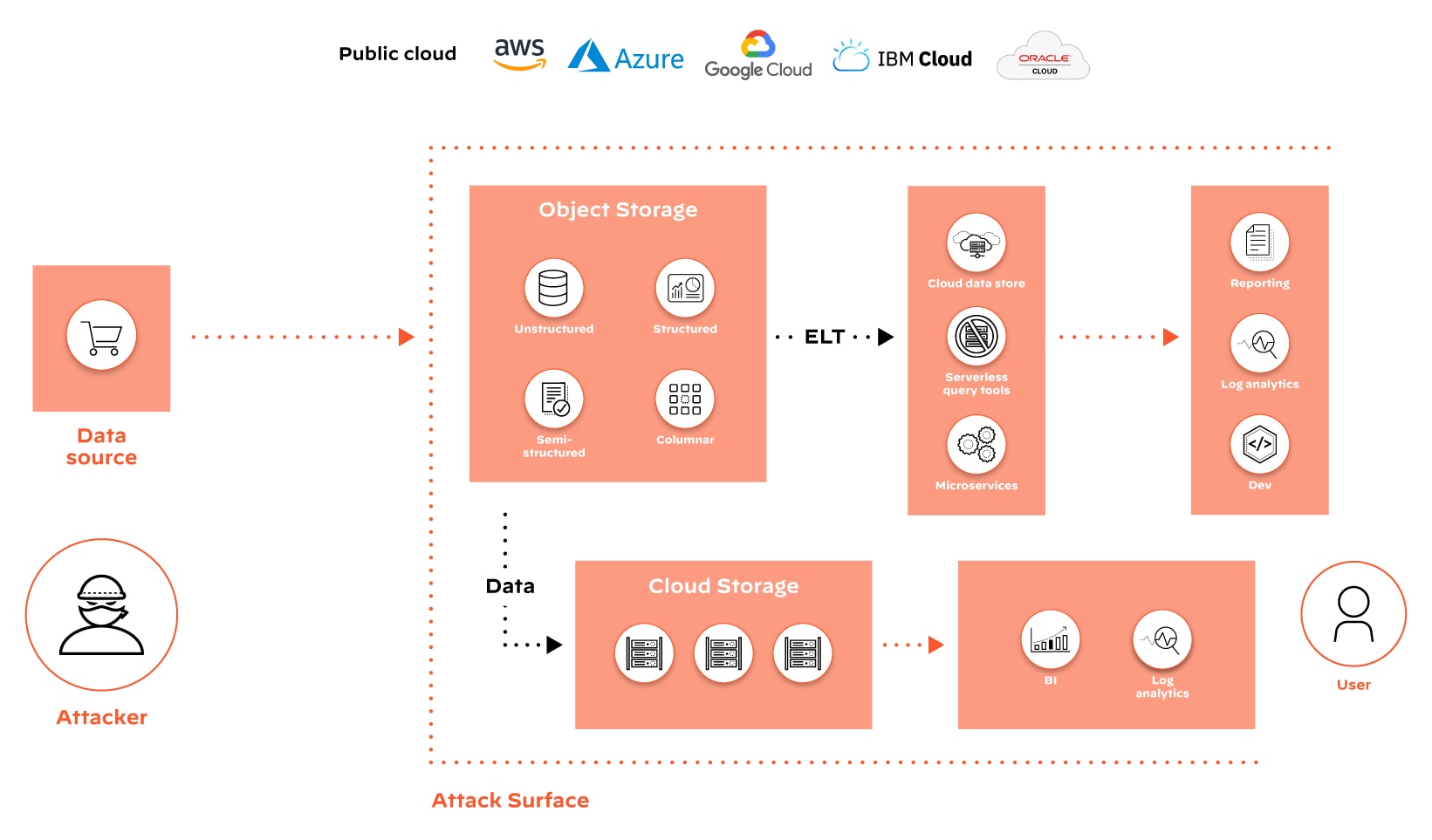
DSPM Capabilities
Projected by Gartner, “By 2026, more than 20% of organizations will deploy DSPM, due to the urgent need to find previously unknown data repositories and their geographic locations to help mitigate security and privacy risks.”
Comprehensive Data Discovery
By scanning cloud environments and on-premises datastores to locate and catalog data assets, DSPM tools play a vital role in discovering shadow data and enabling organizations to understand and address their attack surface.
Shadow data refers to information created, stored, and processed outside of an organization's official IT systems, often without the knowledge or consent of IT departments. By incorporating data discovery in DSPM, organizations can identify and locate shadow data sources across their infrastructure — whether in unauthorized cloud services, personal devices, and third-party applications.
Understanding the data landscape and implementing encryption, access control, data loss prevention, and other appropriate security controls depends on gaining visibility into all the information an organization possesses, including shadow data.
Data Classification Advantage
The active data classification process within data security posture management enables organizations to focus their security resources on the most critical information assets via a targeted approach that ensures sensitive data receives the appropriate level of protection.
Data classification also helps organizations adhere to data protection regulations, as different types of data may require specific security controls to maintain compliance. By understanding the sensitivity and regulatory requirements of their data, organizations can implement custom measures.
Access Governance
Access governance is a key feature of DSPM. It involves managing who has access to what data and ensuring that access rights are granted based on the principle of least privilege, which states that individuals should have access only to the data they need to perform their job functions. DSPM helps organizations to enforce this principle by providing visibility into access controls and identifying instances of excessive or inappropriate access.
Vulnerability and Misconfiguration Detection and Remediation
A key strength of DSPM lies in its capacity for risk detection. By continuously scanning data sources such as databases, file systems, and cloud storage, a DSPM solution can uncover hidden vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that may expose sensitive data to unauthorized access or leakage.
DSPM can detect abnormal user behavior, access patterns, and data movement, which may indicate potential insider threats or external attacks. By providing real-time alerts and actionable insights, DSPM solutions enable organizations to respond quickly to emerging risks and prevent data breaches before they occur.
Compliance Support
Noncompliance with data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA poses significant monetary fines and penalties. By providing visibility into data assets and security controls, DSPM helps organizations meet regulatory standards and demonstrate their compliance with PCI DSS and other data protection regulations. They can also monitor for noncompliance and alert the security team to issues they need to address.
Static Risk Analysis
DSPM tools use static risk analysis to identify potential data risks, which involves analyzing data at rest to identify sensitive information, assess its risk level, and determine if it is adequately protected. By identifying data risks, organizations can prioritize their security efforts and take action to mitigate these risks.
Policy Controls
Data security posture management provides capabilities for policy control, allowing organizations to define security policies that specify how data should be protected and who should have access to it. It will then apply the defined controls — which might include encryption, tokenization, access restrictions — and enforce them across the organization's datastores, ensuring consistent data protection and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
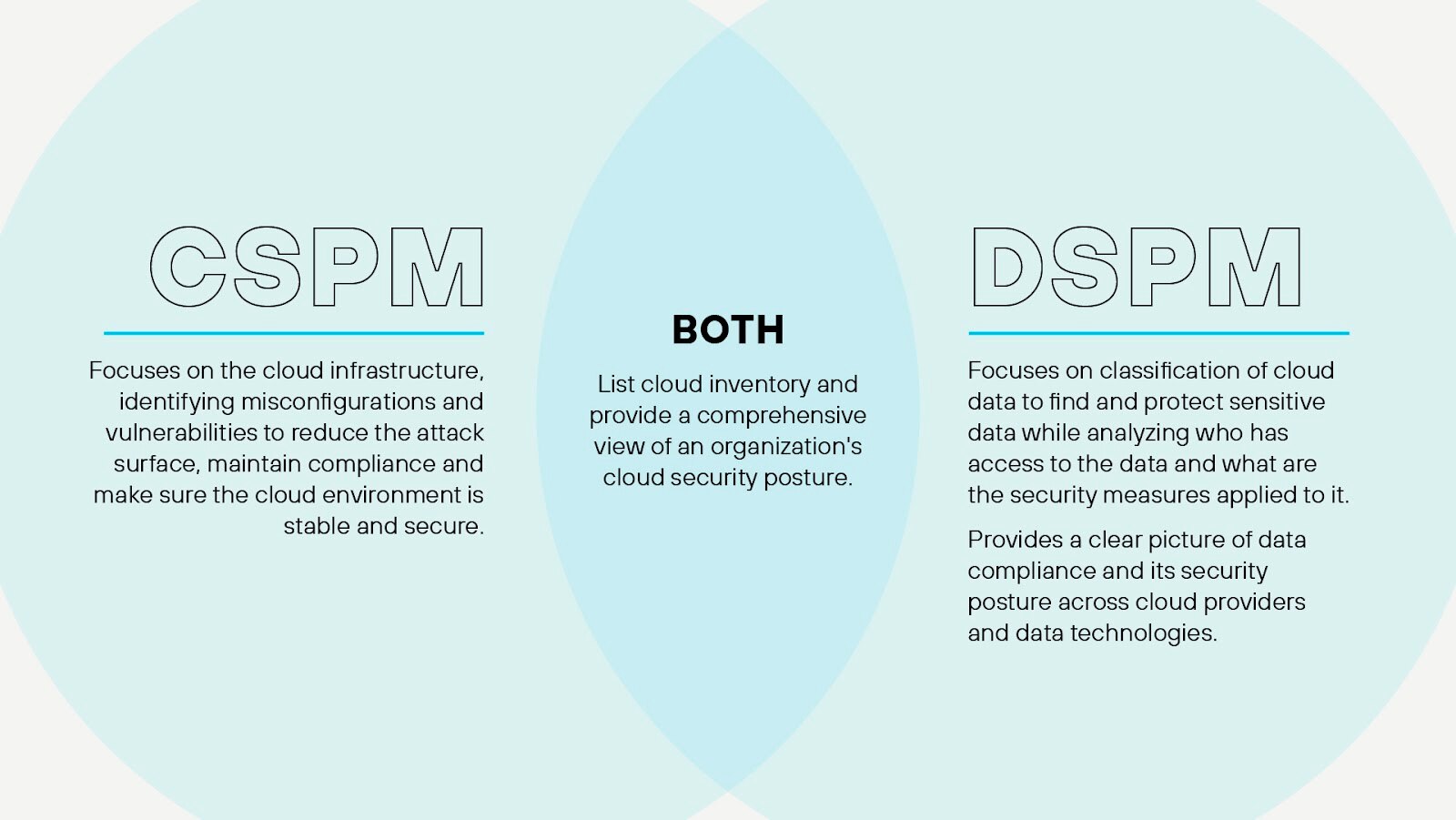
DSPM Vs. CSPM
While DSPM and cloud security posture management (CSPM) both contribute to an organization's overall security posture, they address different aspects of information security.
CSPM focuses on the continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement of an organization's security posture within a cloud computing environment. Organizations rely on CSPM solutions to identify and remediate misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations in cloud-based infrastructures, such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
CSPM — typically integrated into cloud-native application platforms — leverage APIs, automation, and machine learning to collect and analyze data from various cloud resources, including virtual machines, storage, networks, and applications. They evaluate the security configurations and settings of these resources against industry-standard benchmarks, best practices, and regulatory requirements, such as CIS, NIST, GDPR, and HIPAA. By identifying deviations from the established security baselines, CSPM solutions enable organizations to prioritize and remediate security risks in a timely manner.
While CSPM safeguards the cloud environment, DSPM safeguards the data within the environment. Its many components work together to identify sensitive data, classify it according to its level of sensitivity, apply appropriate encryption and access controls, and continuously monitor for potential data exfiltration or unauthorized activities. DSPM solutions also provide reporting and auditing capabilities to help organizations track data usage, demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards, and identify areas for improvement.
Both technologies play a vital role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization's critical assets, and the combined implementation of CSPM and DSPM can significantly enhance an organization's security posture.
DSPM Use Cases
Catalog Data Assets
With DSPM, organizations can quickly locate and catalog their data assets, even in complex multicloud environments. DSPM tools can also classify data based on its sensitivity, helping to prioritize security efforts and ensure that sensitive data is adequately protected.
Assess and Address the Attack Surface
By providing visibility into where sensitive data resides and who has access to it, DSPM tools help to identify potential attack vectors and take steps to minimize the attack surface. This can significantly reduce the risk of a data breach and help to protect the organization's reputation.
Enforce Least Privilege
Organizations use DSPM to track data access permissions and enforce the principle of least privilege. DSPM tools provide visibility into who has access to what data and identify instances of excessive or inappropriate access — both of which assist with the implementation of appropriate access controls.
Streamline Data Security in Multicloud Environments
Enterprises operating in multicloud environments — leveraging services from Google Cloud, AWS, Azure, and other cloud providers — quickly encounter the challenges of managing data security across platforms. DSPM streamlines data management processes by providing a unified view of all data assets, regardless of where they reside. Many organizations rely on DSPM to discover and classify data across multicloud environments, enforce consistent security policies, and provide real-time visibility into their data security posture.
Enhance Data Protection in a Cloud-First Strategy
For organizations adopting a cloud-first strategy, DSPM can help ensure that data security isn’t compromised in the transition to the cloud. DSPM can discover and classify data as it’s moved to the cloud and identify potential risks. It can also monitor data in real time, alerting the security team to changes that might indicate a security risk.
Implement a Data-First Approach
Organizations that prioritize a data-first approach use DSPM technology for top-tier protection for sensitive data. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that handle large volumes of sensitive data, such as those in the financial or healthcare sectors. DSPM also helps these organizations to ensure and demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations.
Data Security Posture Management Tools
Designed to protect sensitive data, DSPM platforms provide a range of functionalities.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): DPL capabilities consist of monitoring and controlling data movement within an organization, helping prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and breaches.
- Encryption: DSPM solutions provide data encryption and decryption capabilities, safeguarding sensitive data at rest and in transit.
- Identity and access management (IAM): IAM capabilities perform the critical task of managing user identities, authentication, and authorization, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and resources.
- Data masking and anonymization: The inclusion of data masking serves to protect sensitive data by replacing it with fictional or scrambled data, which maintains its structure and format but can't be linked back to the original information.
- Security information and event management (SIEM): SIEM capabilities collect, analyze, and report on security events and incidents to detect threats, perform forensic analysis, and maintain compliance.
- Data classification: DSPM platforms help organizations to identify and categorize sensitive data, allowing for better control and protection.
Selecting the appropriate DSPM solution depends on the organization's requirements and objectives. Cloud-native enterprises working with distributed microservices applications typically opt for the centralized solution of a CNAPP with DSPM capabilities seamlessly integrated. But data security posture management solutions aren’t necessarily one-size-fits-all.
Each organization should choose a DSPM solution that aligns with its unique data security needs and regulatory obligations.
