- 1. Why do organizations switch from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- 2. How is SD-WAN a better alternative to MPLS?
- 3. What are the options for migration from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- 4. Should you use an MSP for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration?
- 5. What are the MPLS to SD-WAN migration challenges you can expect?
- 6. Is there a middle ground between MPLS and SD-WAN?
- 7. If your organization is planning an MPLS to SD-WAN migration, is SASE worth considering?
- 8. How to create a successful MPLS to SD-WAN migration plan
- 9. MPLS to SD-WAN migration FAQs
- Why do organizations switch from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- How is SD-WAN a better alternative to MPLS?
- What are the options for migration from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- Should you use an MSP for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration?
- What are the MPLS to SD-WAN migration challenges you can expect?
- Is there a middle ground between MPLS and SD-WAN?
- If your organization is planning an MPLS to SD-WAN migration, is SASE worth considering?
- How to create a successful MPLS to SD-WAN migration plan
- MPLS to SD-WAN migration FAQs
How to Execute an MPLS to SD-WAN Migration Step-by-Step
- Why do organizations switch from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- How is SD-WAN a better alternative to MPLS?
- What are the options for migration from MPLS to SD-WAN?
- Should you use an MSP for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration?
- What are the MPLS to SD-WAN migration challenges you can expect?
- Is there a middle ground between MPLS and SD-WAN?
- If your organization is planning an MPLS to SD-WAN migration, is SASE worth considering?
- How to create a successful MPLS to SD-WAN migration plan
- MPLS to SD-WAN migration FAQs
Executing a successful MPLS to SD-WAN migration is generally a seven-step process:
- Assess your current network needs
- Establish a performance baseline
- Choose the right SD-WAN provider
- Create a detailed migration plan
- Execute the migration carefully
- Test and monitor post-migration
- Continuously monitor and optimize
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN requires careful planning and execution to avoid disruptions and ensure optimal performance.
Why do organizations switch from MPLS to SD-WAN?
It's common knowledge that modern businesses need to be able to adapt quickly and run smoothly. Managing network infrastructure is no exception.
But before SD-WAN emerged to solve this problem, there was multiprotocol label switching (MPLS).
Historically, MPLS was favored because it’s relatively reliable. Plus, it manages and prioritizes traffic flows pretty efficiently.
MPLS emerged in the 1980s and 1990s, offering a more efficient way to manage and route traffic over vast networks. It became the standard for traditional WANs, known for reliability and quality of service (QoS).
The reason it’s so reliable is because MPLS provides dedicated pathways for data. That’s what ensures the predictable service levels. Which makes it useful for applications requiring stringent latency measures.

However, as cloud computing and SaaS applications grew in popularity in the 2000s and onward—combined with the integration of mobile and IoT devices—the limitations of MPLS started to become problematic.
Today’s organizations need a more flexible, cost-effective solution to handle the increased demand for bandwidth, not to mention the shift towards decentralized applications. Unfortunately, MPLS can be somewhat rigid and cost inefficient in the modern context.
In particular, in a cloud-centric environment, MPLS can be very complex and expensive to manage. And that’s because of the need for hardware installations at each site, plus bandwidth restrictions—which do not scale economically as data demands increase.
This is where SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) becomes an alternative worth considering.
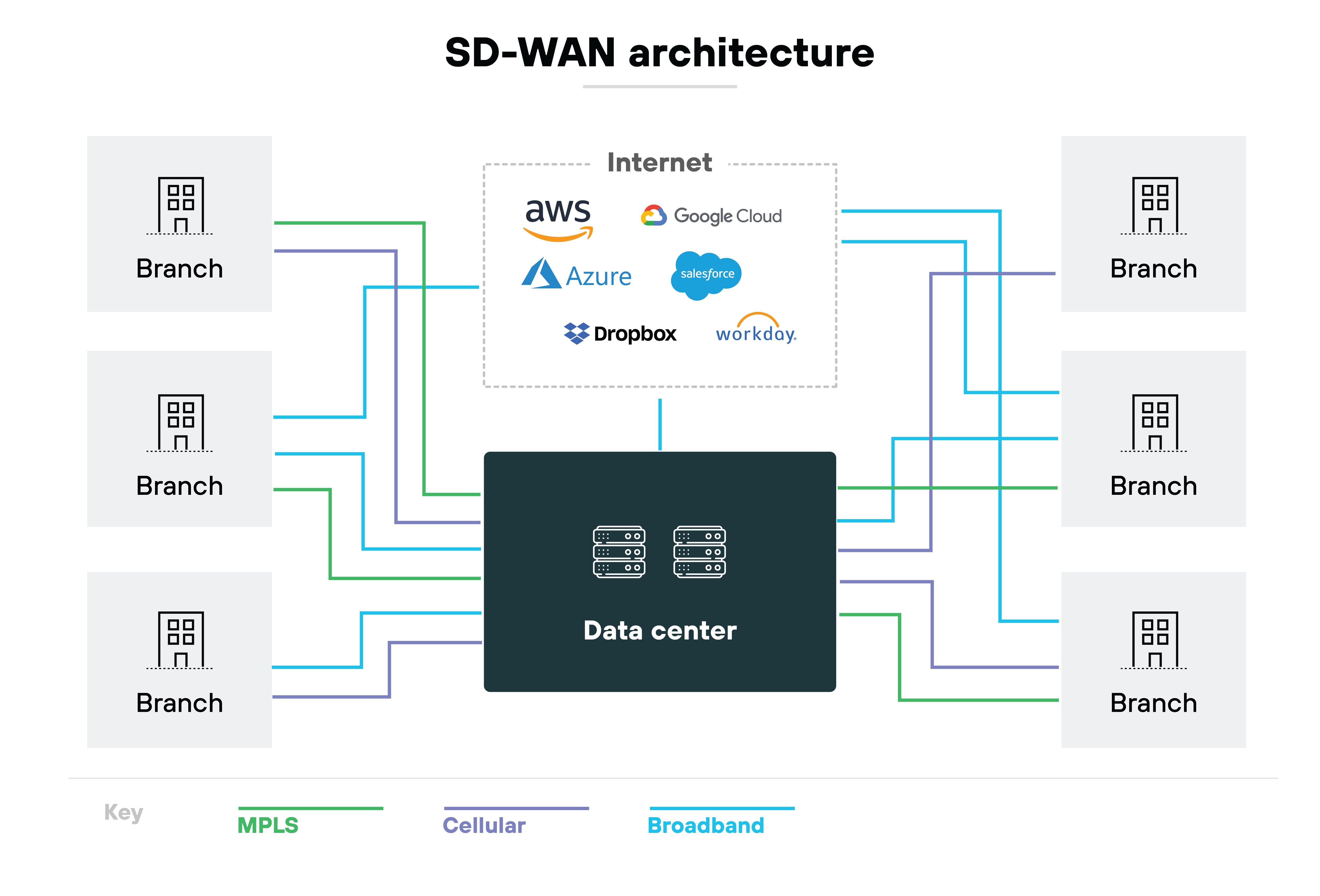
SD-WAN introduces major flexibility and substantial cost-effectiveness when it comes to managing network traffic. Unlike MPLS, SD-WAN doesn’t require physical infrastructure to reroute traffic. The adaptability is crucial for modern businesses that use a variety of cloud-based applications and services.
For example: Consider a typical enterprise using multiple SaaS solutions across different regions. SD-WAN allows for dynamic path selection, which optimizes connectivity and performance by routing traffic through the most efficient paths.
Like this:
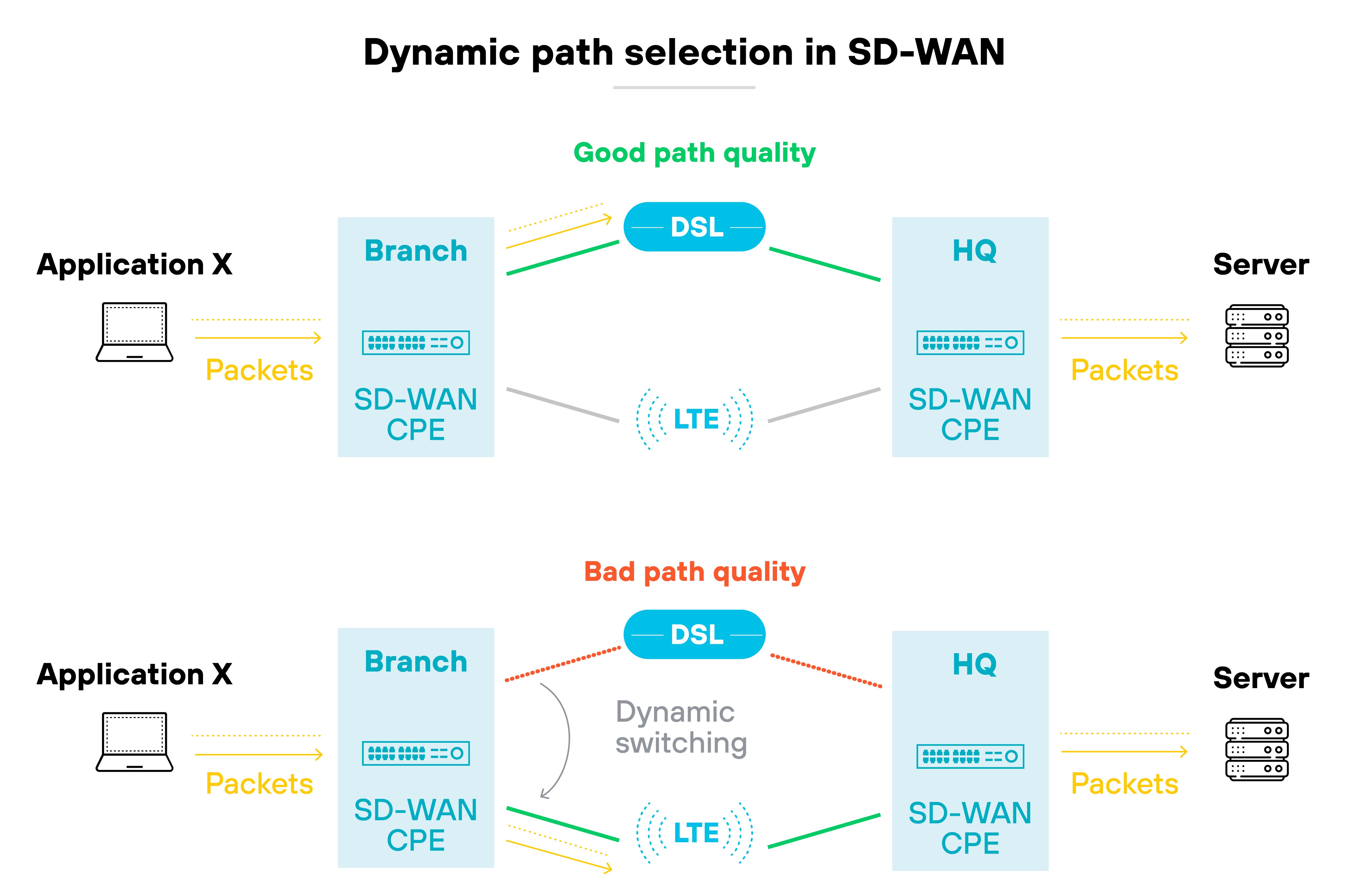
This capability is vital for enhancing the digital experience of users and supporting real-time applications that are sensitive to latency.
Further reading: What Is the Difference Between SD-WAN and MPLS?
How is SD-WAN a better alternative to MPLS?

SD-WAN addresses the limitations of MPLS by offering a solution that aligns with the demands of modern network environments, including:
- Flexibility for modern & remote workforces
- Better cloud connectivity and application integration
- Optimal performance across interconnected systems
- Cost-effectiveness and simplified management
- Decentralized and provider-independent networking
Ultimately, SD-WAN supports the decentralized networks that modern enterprises operate.
It accommodates the high variability in traffic that comes from services like video conferencing, streaming, and real-time collaboration tools. All of which have become commonplace in today's workplace—and are bandwidth intensive.
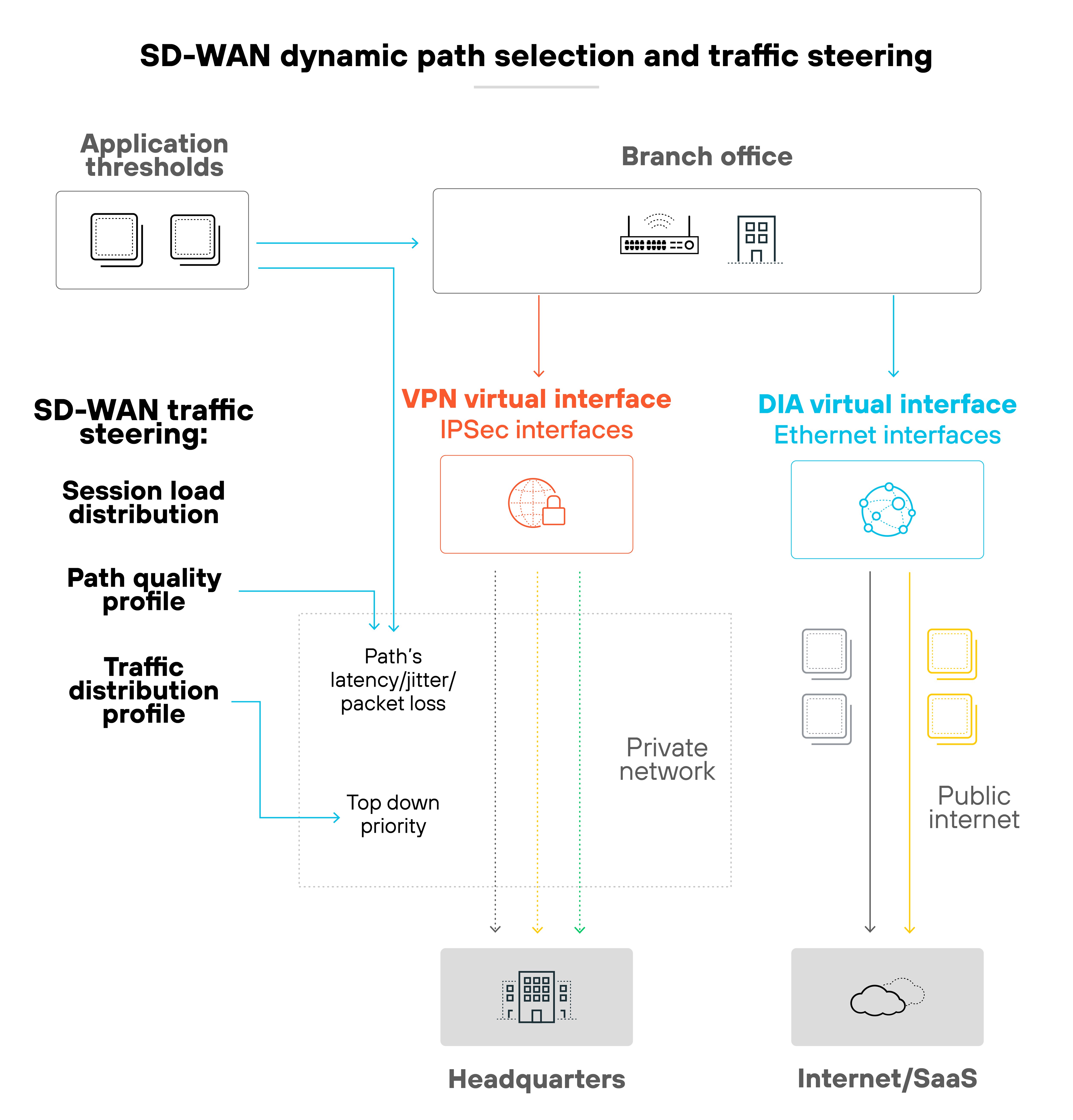
As organizations push for greater digital transformation, the inherent scalability and flexibility offered by SD-WAN become increasingly more important.
But the MPLS migration to SD-WAN isn’t just about adopting new technology.
The unique benefits of SD-WAN allow enterprises to be substantially more agile in their network management. Plus, organizations are in a far better position to respond to network demand changes fast, not to mention opportunities for technological integration.
Flexibility for modern & remote workforces

Nowadays, the modern workforce is increasingly remote. Employees are working from various locations such as their homes, co-working spaces, or even while traveling.
"According to Deloitte, 56% of employed adults work from home at least part of the time. Of these, 22% work fully from home, while 34% maintain a hybrid schedule, blending in-office and remote work. Hybrid workers, on average, spend 3 days in the office and 2.6 days working remotely."
Given the shift to a distributed workforce, traditional office-centric network setups are obviously no longer sufficient. Especially traditionally rigid ones that are often associated with MPLS. Businesses have to be able to adapt quickly to changing network demands. And they also need to be able to provide secure, yet reliable access to corporate resources from anywhere.
SD-WAN adjusts dynamically to support diverse and shifting user demands without the need for complex configurations.
Plus, the rise in cloud-based applications, video conferencing, and collaborative tools requires flexible, scalable network solutions. SD-WAN works well because it can handle fluctuating traffic and provide seamless connectivity, regardless of where employees are working.
Better cloud connectivity and application integration

With a majority of applications now being cloud-based, SD-WAN's ability to offer improved and direct cloud connectivity is increasingly important.
"SaaS (software as a service) applications continues to be the largest category of public cloud services, accounting for approximately 45% of the global cloud market in 2023. The global public cloud services market itself grew by nearly 20% in 2023, reflecting widespread adoption across industries, IDC reported."
Direct access substantially improves cloud application performance and efficiency. MPLS, on the other hand, tends to fall short here. Mostly because its inherent design limitations weren’t intended for cloud integration.
SD-WAN's ability to integrate smoothly with cloud services and external applications supports distributed, modern organizations. Unlike MPLS, which may require special arrangements to connect to cloud infrastructures, SD-WAN facilitates direct and efficient cloud connections. Which equals streamlined access and improved overall network performance.
Optimal performance across interconnected systems
Modern applications are often highly interconnected, which creates new challenges for network performance. SD-WAN’s adaptability plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges. It allows businesses to dynamically route traffic based on real-time needs, ensuring smooth performance across interconnected systems and applications.
This flexibility helps prevent the bottlenecks commonly seen with traditional MPLS setups, especially in complex digital environments where cloud-based applications and real-time collaboration tools are increasingly common. With SD-WAN, networks can adjust automatically to shifting traffic demands, making it easier to maintain optimal performance for critical business processes.
By accommodating the dynamic nature of modern applications, SD-WAN ensures that network resources are used efficiently, improving overall application performance and user experience.
Cost-effectiveness and simplified management

SD-WAN offers a more budget-friendly solution by reducing the need for the proprietary hardware required with MPLS. It also uses existing internet connections, which lowers both installation and operational costs.
Also: SD-WAN simplifies network management through automation, streamlining tasks like traffic routing and policy updates. This allows businesses to scale easily. Adding new sites or adopting new technologies is fairly simple, and certainly without the complexity often associated with MPLS setups.
Note: While it’s true that SD-WAN can help organizations save money on network costs, savings aren’t always guaranteed. The cost of MPLS networks and diverse broadband options vary by location. Plus, initial investments can be substantial, and network complexity along with ongoing management costs can offset savings. The geographical distribution of your locations can influence the complexity and cost of implementing an SD-WAN solution that meets your network connectivity needs.
Further reading: How Much Does SD-WAN Cost?
Decentralized and provider-independent networking
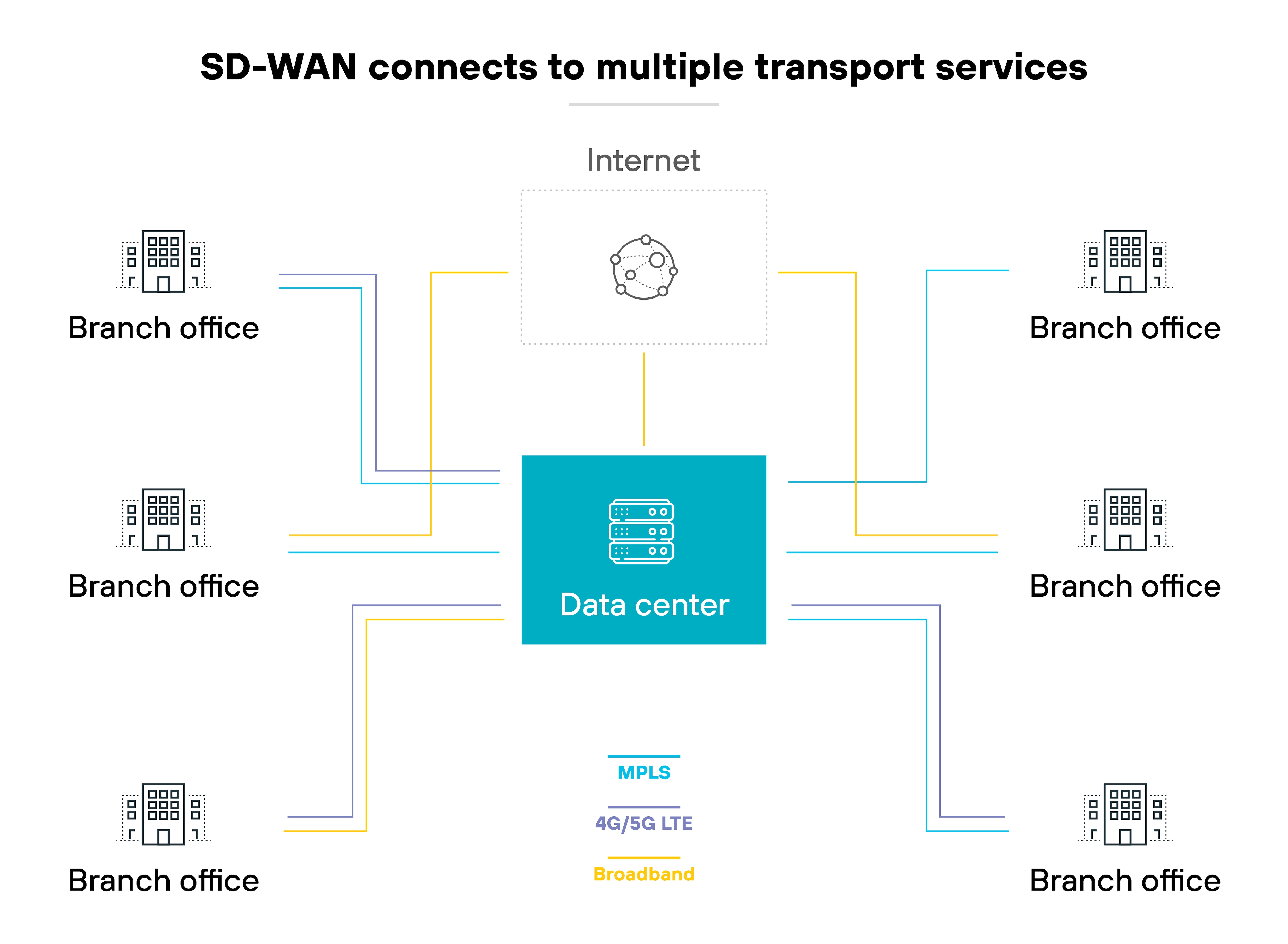
SD-WAN offers independence from traditional service providers. Businesses can configure their WAN based on specific needs without being tied to a single provider. The flexibility ensures that businesses can choose the most suitable, cost-effective service options available.
That’s a stark contrast to MPLS, which often locks organizations into long-term contracts with specific carriers.
What are the options for migration from MPLS to SD-WAN?
When migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN, businesses have several strategies to choose from:
- Augmentation
- Phased
- Rip-and-replace
The choice of migration strategy really depends on a company’s specific needs and network structure. Each approach comes with its own set of pros and cons and varies in complexity and impact.
Let’s take a look at the details of each.
Augmentation MPLS to SD-WAN migration

This option involves running MPLS and SD-WAN side-by-side.
Essentially, the existing MPLS network is maintained, while SD-WAN is introduced gradually to handle specific traffic or applications.
This migration approach is similar to the concept of a hybrid cloud, where both private and public cloud environments coexist.
In this scenario, MPLS is still used for critical traffic, such as voice and video, while SD-WAN manages less sensitive traffic.
This way, businesses can gradually introduce SD-WAN without totally abandoning MPLS infrastructure. It tends to be beneficial for organizations who are more focused on optimizing costs and performance while retaining MPLS for certain tasks.
Rip-and-replace MPLS to SD-WAN migration

A rip-and-replace migration is exactly what it sounds like: organizations completely replace their MPLS circuits with SD-WAN technology.
This option is generally pursued by organizations looking to fully embrace SD-WAN and move away from the high costs of MPLS connections.
By switching completely to SD-WAN, businesses can reduce the expenses associated with MPLS while improving flexibility and scalability.
However, this method does require very careful planning to ensure a smooth transition and avoid any disruptions in network performance.
Phased MPLS to SD-WAN migration

A phased migration allows businesses to gradually migrate their remote sites or locations to SD-WAN.
It starts by migrating the less critical sites first, which gives IT teams the opportunity to identify and resolve any issues early on. As more locations move over to SD-WAN, any obstacles that arise can be addressed. This generally makes for a smoother transition for the critical sites toward the end of the process.
This method is ideal for businesses that prefer taking it a step at a time. It’s worth noting that a phased migration from MPLS to SD-WAN does generally allow for better control and troubleshooting throughout the process.
Should you use an MSP for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration?
Deciding whether to use a managed service provider (MSP) for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration depends on your organization’s needs, resources, and expertise.
Either way, migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is a big transition. It involves shifting from hardware-dependent connections to software-driven networking. And the process can be complex.
MSPs can make the process more efficient and less overwhelming. But they come with a level of dependency that may not be suitable for everyone.
An MSP can potentially help simplify this transition by guiding you through the technical steps and helping you avoid potential pitfalls.
But is it the right choice for your organization?
Let’s break it down.
If your network team has limited experience with SD-WAN, an MSP might be a good fit.
Reputable MSPs bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise in network management. Which means they can handle the setup, configuration, and day-to-day management of your new SD-WAN system. So if you do have an internal network team, they can focus on other important tasks.
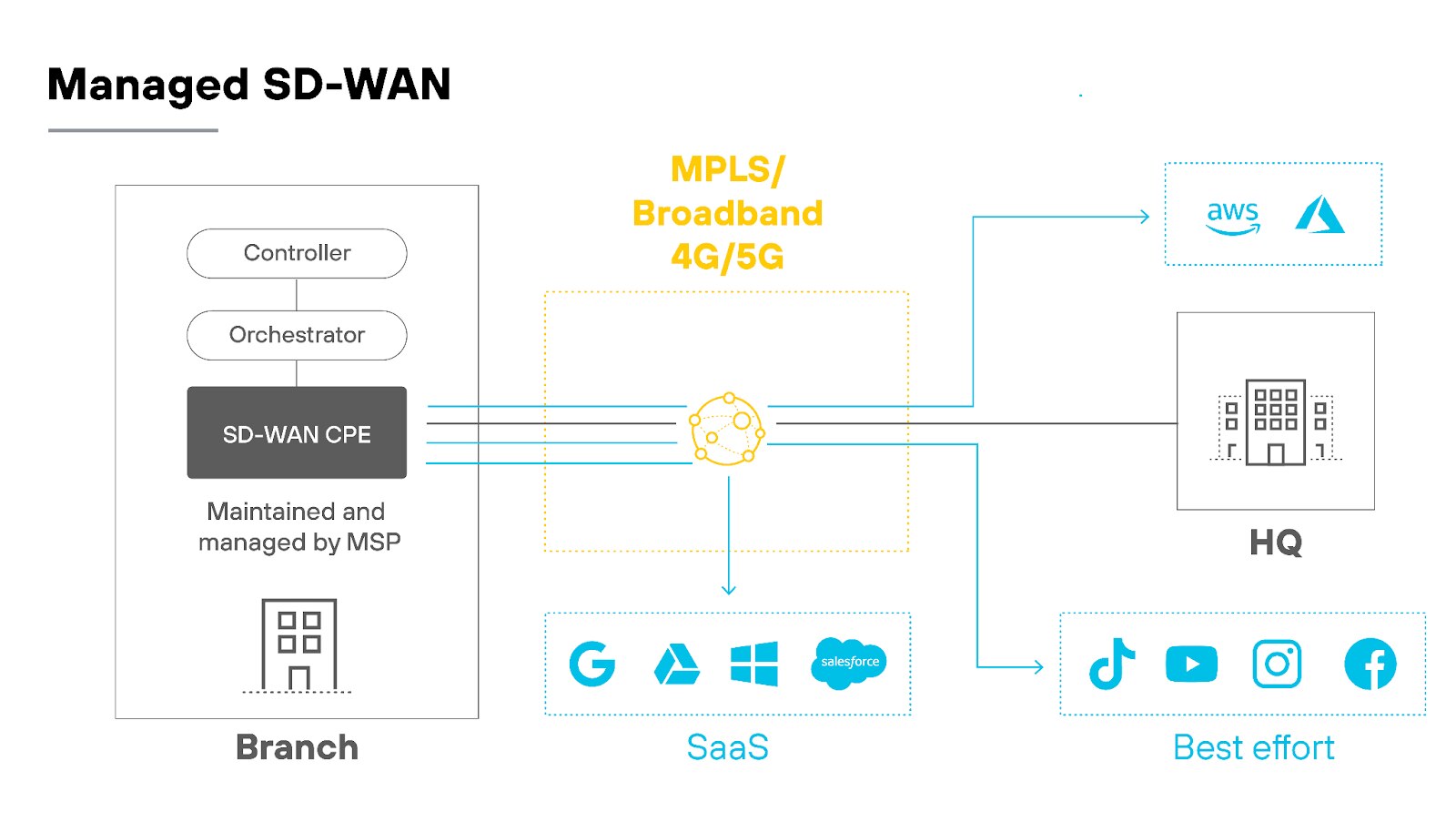
MSPs also have access to the latest technology and can recommend solutions that fit your specific business needs.
Another consideration is vendor neutrality.
MSPs often act as a middleman between businesses and SD-WAN vendors. They can evaluate your network requirements and recommend a solution that fits your infrastructure and budget. While SD-WAN vendors are equally capable of supporting a new SD-WAN customer, the MSP approach may be more comfortable for some organizations who prefer to evaluate multiple options simultaneously from a vendor neutral perspective.
Cost is an additional factor.
For some organizations, MSPs can help reduce costs by outsourcing SD-WAN management versus hiring additional full-time network personnel. This can be financially helpful to businesses that don’t have the resources to build a dedicated in-house team. If you partner with an MSP for your MPLS to SD-WAN migration, you can avoid the expense of extra hires while still benefiting from expert network management.
However, relying on an MSP can also have some downsides.
For instance, you’ll be depending on a third-party provider for your network operations.
Which means that any changes, updates, or troubleshooting will need to go through the MSP, and that could introduce delays.
So if your business requires more direct control over network operations, then an in-house approach might be preferable. You’ll have full control over the network—but may need to invest in training or hiring staff with the right expertise.
Weigh the pros and cons carefully to determine the best path forward for your migration.
Further reading:
What are the MPLS to SD-WAN migration challenges you can expect?

Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is a major commitment. As with any major infrastructure shift, there are challenges that you can expect to encounter along the way. The good news is that understanding the hurdles upfront can help in planning and executing a smoother migration.
Hardware compatibility issues
One challenge you may face during the migration is compatibility with your current hardware.
Plenty of businesses have legacy equipment that isn’t optimized for SD-WAN.
For example: Older routers and switches might not support necessary updates or have the processing power to handle SD-WAN traffic.
This could mean additional expenses to upgrade or retrofit your SD-WAN hardware. On the other hand, if you choose not to upgrade, you may experience issues with network performance or stability.
Bandwidth variability
SD-WAN relies on public internet connections. Which means bandwidth can fluctuate depending on network congestion and ISP performance.
MPLS, by contrast, offers more predictable, guaranteed bandwidth. So, with SD-WAN, careful planning is needed to ensure critical applications get the resources they need.
If not managed well, your network performance could suffer during peak times, affecting operations.
Security considerations
When moving from MPLS to SD-WAN, security becomes a higher priority.
MPLS uses private, controlled paths, while SD-WAN leverages the public internet. This exposure means you’ll need to focus more on encryption and security features to protect your data.
Integrating next-gen firewalls and other security measures is critical. However, balancing these security layers with network performance can be tricky.
Deployment complexity
Deploying SD-WAN can be tricky.
It’s worth noting that zero touch provisioning (ZTP) is designed to simplify the process. But setting it up correctly can be complex. A lot depends on the initial configuration. Especially for organizations with multiple locations.
You’ll also need to retrain your IT and/or network staff to manage the new system.
In short, even though ZTP reduces manual setup later, the early stages of deployment require careful planning.
Network policy configuration
SD-WAN offers the flexibility to prioritize different types of traffic. Which is great. But it also requires setting up detailed policies to ensure your critical applications get the bandwidth they need.
For example: You might need to prioritize video conferencing over email traffic. Creating these policies can be a challenge, particularly in larger, more complex networks.
The key is balancing your bandwidth across all applications without causing disruptions.
Skill gaps in network teams
SD-WAN technology is different from MPLS. Which means your network team will likely need training on the new system.
Without this knowledge, migration could slow down, and troubleshooting issues may become more difficult. In some cases, it might be necessary to bring in outside expertise or rely on a managed service provider (MSP) for support. And that adds time and potential costs to the project.
Monitoring and visibility
As explained, SD-WAN paths are dynamic. They can change in real-time based on traffic conditions.
Traditional monitoring tools might not offer the level of detail needed to track these changes effectively. So, ensuring that your IT team has access to advanced monitoring tools is essential.
Otherwise, visibility gaps could leave you in the dark about performance issues until they start to affect operations.
Is there a middle ground between MPLS and SD-WAN?
Yes, there are ways to achieve a middle ground between MPLS and SD-WAN.
One particular method, known as hybrid SD-WAN, combines SD-WAN technology with traditional MPLS by integrating it with other connection types like broadband and LTE to create a versatile, efficient network architecture.

It tends to be a good fit for organizations that still depend on MPLS for critical applications but want to add the flexibility and cost savings that SD-WAN offers.
Here’s how hybrid SD-WAN works:

SD-WAN acts as an overlay, increasing network flexibility and control by using software to manage virtual layers over existing physical networks. This allows organizations to dynamically direct and reroute traffic based on the specific requirements of different applications.
MPLS, on the other hand, serves as the underlay, offering reliable and stable connections crucial for high-priority or sensitive data transfers.
Keeping MPLS within a hybrid model ensures high-performance connections for tasks that need consistent bandwidth or low latency, like critical applications.
This hybrid approach enables the physical infrastructure to reliably support essential business functions.
Further reading: What Is Hybrid SD-WAN?
If your organization is planning an MPLS to SD-WAN migration, is SASE worth considering?
If your organization is planning an MPLS to SD-WAN migration, SASE is absolutely worth considering before you move forward.
When planning an SD-WAN migration of any kind, it’s important to think about whether your organization’s network security needs are evolving as well.
Secure access service edge (SASE) combines SD-WAN with cloud-native security, including features like secure web gateways, firewalls, and zero-trust network access.

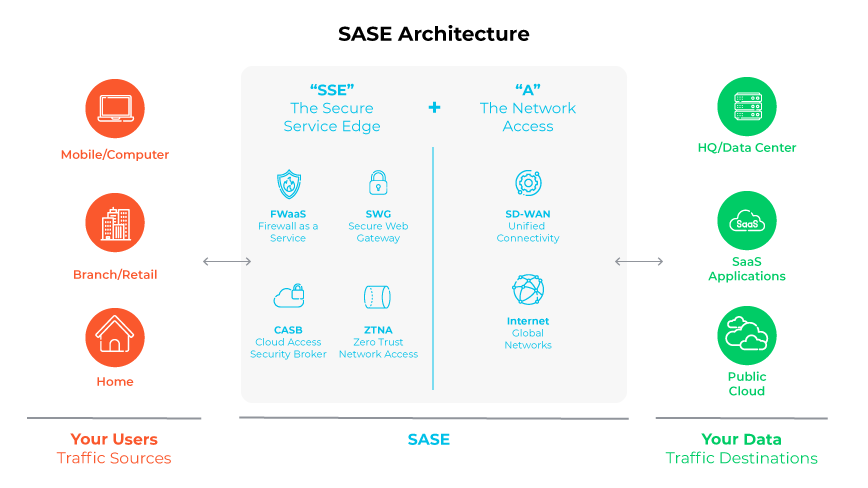
For organizations that want a future-proof solution, are managing decentralized workforces, and/or are cloud first, SASE could be a better long-term option. It definitely offers a more comprehensive approach to network and security. Especially for businesses looking to streamline management and security enforcement across all locations and users.
Further reading: SASE vs. SD-WAN: What's the Difference?
How to create a successful MPLS to SD-WAN migration plan

Transitioning from MPLS to SD-WAN can bring significant benefits, but a successful migration requires careful planning and execution. A step-by-step plan will help you make sure you cover all the necessary components, avoid disruptions, and meet your network goals.
Here’s how to create a successful migration plan.
Step 1: Assess your current network needs
Start by evaluating your existing network setup.
You’ll need to document your bandwidth requirements, the applications you rely on, and where your users are located. This documentation will guide you in selecting the best SD-WAN solution.
A clear view of your network topology—how your sites and components are connected—is essential.
Additionally, take note of your business-critical applications so you can prioritize them during migration to minimize any disruption to operations.
Tip Always factor in the potential for future growth when determining the scalability and capacity requirements of your SD-WAN solution. To optimize costs effectively, you need to balance current needs with long-term objectives.
Step 2: Establish a performance baseline
Before beginning your migration, it’s important to benchmark your network’s current performance.
This means tracking metrics for both private and cloud-based applications, including:
- Latency
- Packet loss
- User experience
Like so:

These benchmarks will serve as your performance baseline, allowing you to measure improvements after SD-WAN implementation.
A solid understanding of your current performance will also help you determine the effectiveness of the migration and ensure the project meets organizational expectations.
Step 3: Choose the right SD-WAN provider

The provider you choose plays a critical role in the success of your migration.
You’ll need to evaluate various SD-WAN providers based on features, pricing, and support.
Consider whether you need fully managed, co-managed, or self-managed services based on your IT team’s expertise and your business needs.
The right provider should be able to support your critical applications, ensure high performance, and offer the flexibility you need.
Further reading:
Step 4: Create a detailed migration plan
Once you’ve assessed your network and chosen a provider, the next step is to create a detailed migration plan.
Decide on the order of site migration. It’s often a good idea to start with less critical locations to work out any potential issues before moving to more important sites.
Coordination is also super important during this phase—so make sure to communicate your migration timeline to all relevant stakeholders, from your IT team to business users. Everyone needs to be adequately prepared for any changes.
Step 5: Execute the MPLS to SD-WAN migration carefully
During the MPLS migration to SD-WAN, it’s important to proceed in a controlled, methodical manner. This may seem obvious, but it's easy to overlook smaller details that can cause disruptions if not properly managed
Migrate one site at a time, ensuring that branch offices and internet access points are properly configured to avoid disruptions.
Tip As each site is moved from MPLS to SD-WAN, test the new setup thoroughly. This includes confirming that traffic is routed properly and key applications perform as expected. Testing as you go ensures that each migration step is successful before moving on to the next.
Step 6: Test and monitor post-migration
After completing the migration, perform extensive testing to ensure the new network is functioning as expected across branch offices, data centers, and cloud applications.
Compare the post-migration performance to the baseline you established earlier.
This testing phase helps confirm that the SD-WAN solution is delivering the benefits you anticipated.
Step 7: Continuously monitor and optimize
Once your SD-WAN migration is complete, the process doesn’t end.
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure your new SD-WAN solution continues to perform well.
Monitor traffic patterns, identify any bottlenecks, and adjust policies as needed to optimize performance.
Ongoing monitoring and optimization help you catch issues early and make necessary adjustments to maintain network health.




